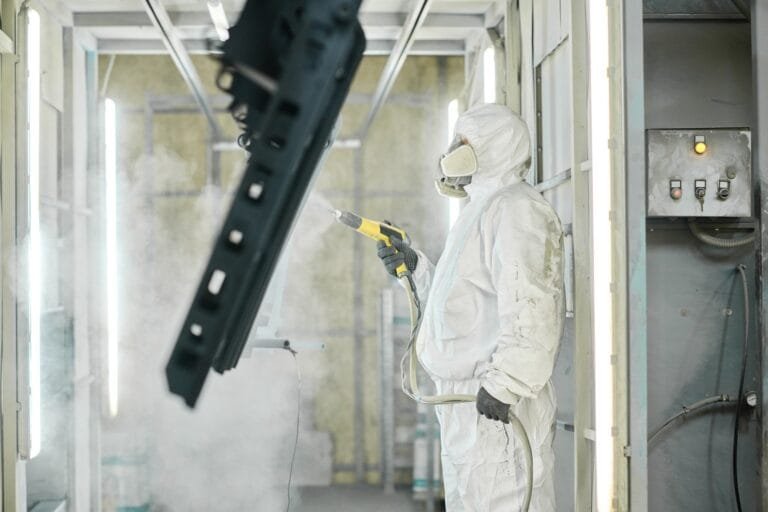
Why Aluminum Powder Coating Matters
In modern manufacturing, aluminum has become the material of choice for everything from automotive wheels and aerospace components to architectural facades and consumer electronics. But aluminum alone can’t always stand up to harsh environments or meet demanding aesthetic standards. Enter powder coating—a powerful solution to protect and enhance aluminum’s performance and appearance.
Powder coating involves applying a dry polymer powder electrostatically onto aluminum parts, then curing the coating under heat to create a durable, long-lasting finish. The result? Outstanding corrosion protection, aesthetic appeal, and sustainability. But can you powder coat aluminum effectively? Absolutely.
- Why Aluminum Powder Coating Matters
- Can You Powder Coat Aluminum?
- The Aluminum Powder Coating Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Advantages Over Conventional Coating Processes
- Quantified Benefits of Powder Coating Aluminum
- Powder Coating vs. Anodizing vs. Wet Paint
- Cost of Aluminum Powder Coating vs. Traditional Finishes
- Choosing the Right Powder Coating Service (Professional Checklist)
- What Are Aluminum Powder Coating Colors?
- Common FAQs on Powder Coating Aluminum
- Conclusion: Maximizing Aluminum’s Potential with Powder Coating
- Work With CastMold
- Crafting Excellence, Together
Can You Powder Coat Aluminum?
Yes, aluminum can be powder coated—and it’s one of the best finishing methods available. With proper preparation and curing techniques, powder coating provides aluminum with a corrosion-resistant, highly durable, and aesthetically pleasing finish, capable of lasting decades in harsh conditions.
In this guide, I’ll take you through every essential detail of aluminum powder coating, including processes, benefits, costs, best practices, and common questions—so you can make informed decisions for your industrial needs.
The Aluminum Powder Coating Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Proper powder coating on aluminum isn’t just about spraying powder; it’s a meticulous, multi-step process. Let’s walk through each critical step in detail:
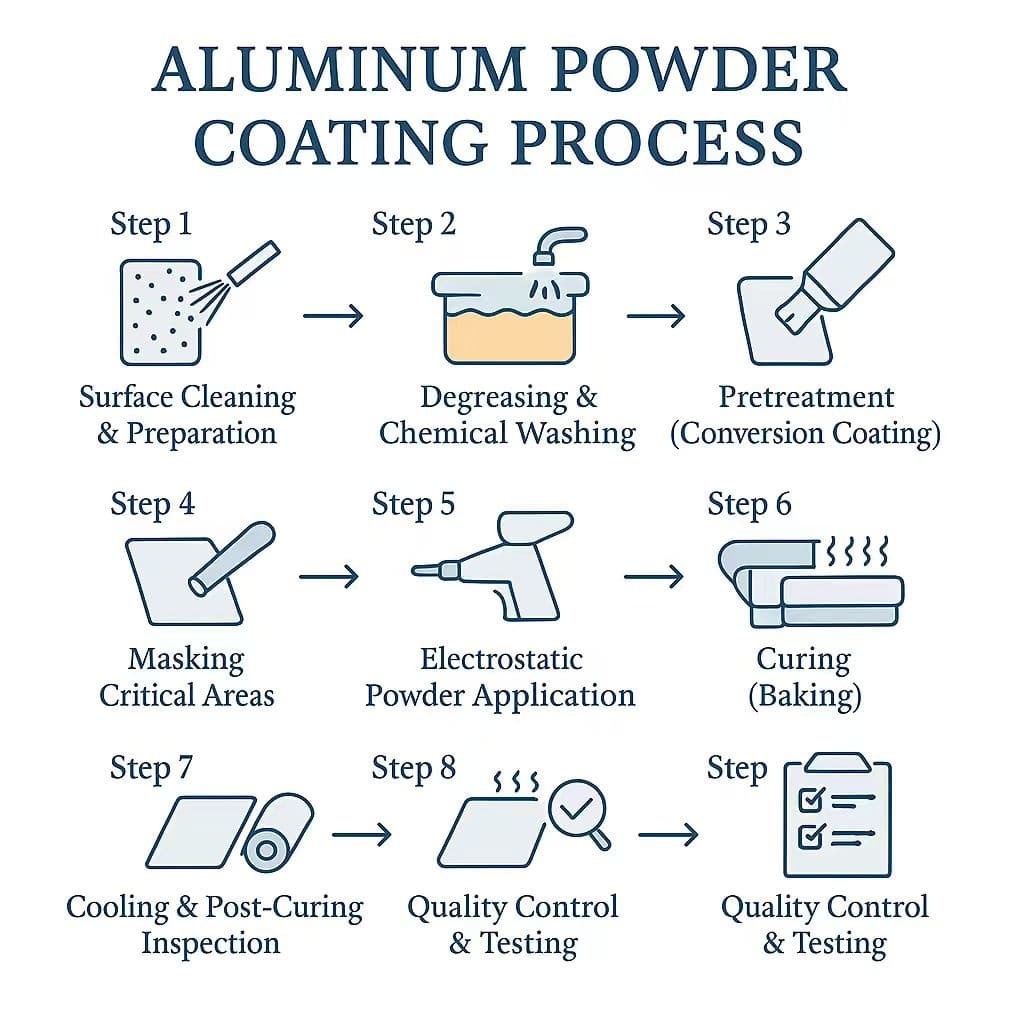
Step 1: Surface Cleaning & Preparation
Great powder coating starts with thorough cleaning. Any contaminants (grease, oil, oxides, or dust) can compromise adhesion. Typically, aluminum parts undergo abrasive blasting (using aluminum oxide or garnet media) to remove previous finishes and contaminants, leaving a uniform anchor profile (~50 microns) to ensure strong adhesion.
Step 2: Degreasing & Chemical Washing
After blasting, aluminum components undergo a chemical wash in alkaline cleaning solutions to strip residual oils. Thorough rinsing follows to neutralize the surface, leaving the aluminum immaculately clean. Any remaining oils or grease can cause bubbling and flaking, so this step is critical.
Step 3: Pretreatment (Conversion Coating)
Pretreatment is perhaps the most crucial step for aluminum powder coating durability. The goal is to convert the aluminum surface chemically to promote excellent powder adhesion and corrosion resistance. Popular pretreatments include zirconium-based and phosphate conversion coatings, which can dramatically increase corrosion resistance (often exceeding 1,000 hours in salt spray tests).
Step 4: Masking Critical Areas
Certain aluminum parts may require masking threads, mating surfaces, or tight tolerances. High-temperature silicone masking tapes and plugs protect areas from unwanted coating, ensuring parts fit precisely after curing. Proper masking reduces costly post-coating machining.
Step 5: Electrostatic Powder Application
The cleaned and pretreated aluminum is now ready for powder coating. An electrostatic spray gun charges the polymer powder particles (typically 60-90 kV), which adhere evenly to the grounded aluminum substrate. Thanks to electrostatic attraction, even complex shapes and recesses receive uniform coverage. Powder coatings are typically applied at a thickness between 50-100 microns (2-4 mils).
Step 6: Curing (Baking)
After application, the coated aluminum parts move into a curing oven at 180-200°C (350-400°F). The powder particles melt, flow, and chemically cross-link, creating a seamless, tough polymer layer. Accurate oven temperature and cure time (usually 15-25 minutes) are vital—too short or too long can compromise coating performance.
Step 7: Cooling and Post-Curing Inspection
Once curing is complete, parts are cooled to room temperature. Controlled cooling prevents coating defects such as cracking or delamination. After cooling, quality inspections confirm coating thickness, adhesion (ASTM D3359 cross-hatch test), and visual consistency.
Step 8: Quality Control & Testing
A reputable powder coating service verifies final coatings meticulously. Standard tests include film thickness measurement, adhesion tests, impact resistance checks, and corrosion resistance evaluations (ASTM B117 salt spray). Parts only ship after rigorous validation.
- Powder coatings are solvent-free and emit negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs), eliminating the need for expensive pollution control equipment and enabling easier compliance with environmental regulations such as those from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
- They can produce significantly thicker coating films compared to traditional liquid coatings without issues like sagging or running, resulting in enhanced durability.
- Powder-coated surfaces exhibit superior uniformity, with minimal visual differences between horizontal and vertical applications, unlike liquid coatings which often show variation.
- The technology allows for a wide array of specialty effects that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other coating methods.
- Curing times are substantially shorter than those of liquid coatings, especially when using ultraviolet (UV) cured powders or advanced low-bake thermosetting powders, leading to increased production efficiency.
Quantified Benefits of Powder Coating Aluminum
Choosing powder coating for aluminum isn’t just about aesthetics—it provides measurable, quantifiable advantages:
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Properly powder-coated aluminum commonly withstands 1,000+ hours in salt spray tests without signs of corrosion—essential for outdoor and marine applications.
- Exceptional Durability: Powder coating is chip, scratch, and impact-resistant. Tests demonstrate powder coatings outperform wet paints by nearly double the lifespan—lasting upwards of 15-20 years.
- High Material Efficiency & Sustainability: Powder coating processes reclaim overspray, achieving up to 95% material utilization, significantly outperforming traditional paints. Zero solvents mean virtually no VOC emissions, aligning with strict environmental regulations.
- Aesthetic Versatility: Hundreds of colors, textures, and finishes are available. Powder coating can mimic metallic, glossy, matte, and textured finishes consistently—critical for industrial designers and branding.
- Cost-Effective in High Volumes: Although initial setup may be higher than wet paint, powder coating quickly becomes cost-effective for batch production, offering long-term cost savings through durability and lower maintenance requirements.
Powder Coating vs. Anodizing vs. Wet Paint
Choosing the right finish depends on your application’s needs:
| Factor | Powder Coating | Anodizing | Wet Paint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent (chip-resistant) | Outstanding (integral oxide) | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (1000h salt spray) | Excellent (oxide layer) | Moderate (with primers) |
| Aesthetics & Color Range | Very versatile (hundreds of colors) | Limited (metallic colors only) | Highly versatile (unlimited) |
| Environmental Safety | Excellent (low VOC) | Good (chemically intensive) | Poor (high VOC) |
| Ideal Use | Industrial, automotive, architectural | Aerospace, precision components | On-site, large or artistic jobs |
Powder coating generally provides the best balance between durability, aesthetic variety, and environmental safety, especially for large-volume industrial parts.
Cost of Aluminum Powder Coating vs. Traditional Finishes
To understand the cost-benefit analysis, let’s examine typical cost ranges:
| Job Type/Scale | Powder Coating Cost (USD) | Wet Paint Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Single Small Part | $20-40 per part | $10-30 per part |
| Batch of 100 Parts | $3-8 per part | $3-6 per part |
| Automotive Wheels (Set of 4) | $400-600 total | $200-400 total |
While powder coating initially may seem more expensive, the reduced need for maintenance, repairs, and repainting makes it the most cost-effective long-term solution for industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Powder Coating Service (Professional Checklist)
Selecting a powder coating provider isn’t trivial—here’s what you need to check:
- Aluminum-specific pretreatment capabilities
- ISO 9001 certification and industry-specific standards compliance
- Proven quality testing procedures (adhesion, thickness, corrosion)
- Proper oven control and temperature accuracy
- Experience with aluminum alloys and specific application references
- Transparent documentation and reporting of quality inspections
A reputable service will meet all these criteria, ensuring your aluminum parts receive top-notch powder coating.
What Are Aluminum Powder Coating Colors?
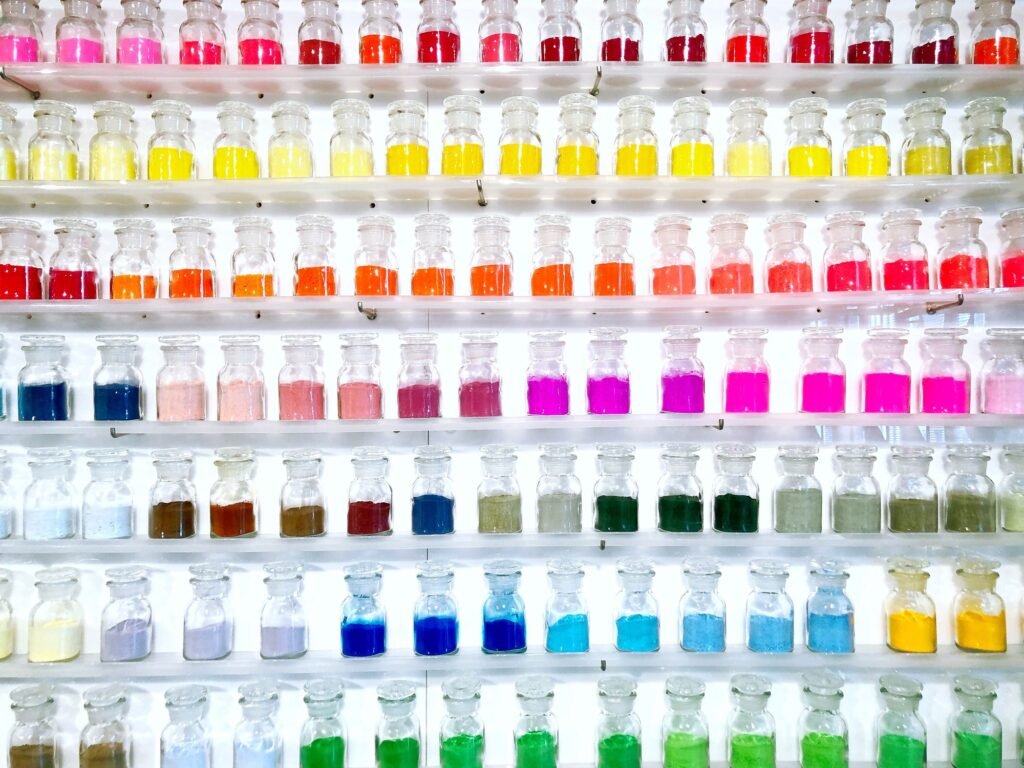

Aluminum powder coating offers a diverse palette of colors and finishes, meeting both aesthetic and functional needs across industries. Here are the main types of available options:
- Solid colors: Common choices include white, black, grey, blue, red, and green—widely used in architecture, automotive, and consumer products.
- Metallic effects: Finishes like silver, gold, bronze, brass, and copper create a premium appearance, popular for electronics, furniture, and signage.
- Gloss levels: Available in high gloss, semi-gloss, satin, and matte to suit different visual and tactile preferences.
- Special textures: Options include wrinkle, hammered, sandtex, and antique textures for added depth and surface character.
- RAL & Pantone systems: Most suppliers offer standardized RAL colors and Pantone matching services for brand consistency and project-specific needs.
- Custom colors: Tailored color development is possible for specialized applications, with options for heat resistance, UV stability, and outdoor durability.
These coating colors don’t just improve appearance—they also contribute to corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and long-term performance. That’s why aluminum powder coating is widely applied in industries like automotive, architecture, consumer electronics, and industrial machinery.
Common FAQs on Powder Coating Aluminum
Conclusion: Maximizing Aluminum’s Potential with Powder Coating
Aluminum powder coating isn’t just a finishing process—it’s a strategic decision that improves durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. By clearly understanding its processes, benefits, and practical considerations, you’re better equipped to leverage this powerful finishing solution for your products.
Powder coating is the future of aluminum finishing, promising superior performance, greater cost-effectiveness, and sustainability—all critical factors in today’s competitive industrial markets. Embrace it wisely, and your aluminum products will stand out in quality, performance, and longevity.
Work With CastMold
At CastMold, we provide integrated services of aluminum die casting and surface finishing, delivering high-precision parts with professional craftsmanship—all from a single trusted supplier.