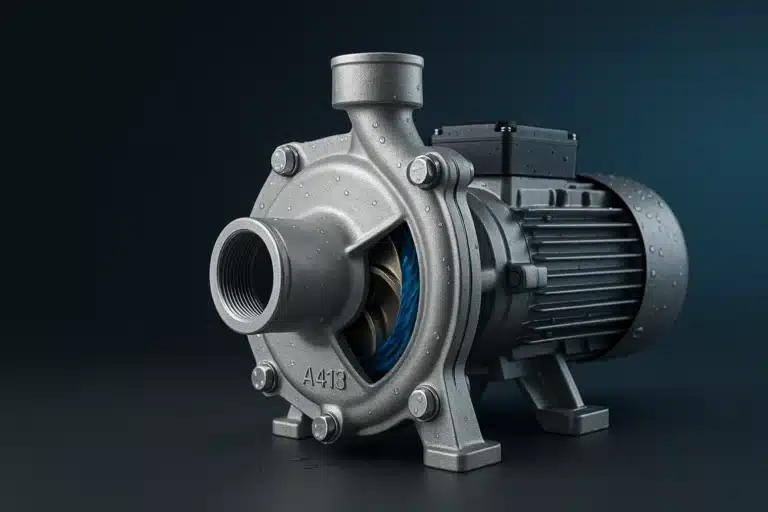
A413 aluminum alloy, a standout in the 4xx.x series, is a premier choice for high-pressure die casting (HPDC) applications where pressure tightness is non-negotiable. Manufacturing engineers and product designers specify this eutectic aluminum-silicon alloy for its exceptional fluidity, allowing it to fill intricate, thin-walled cavities with precision. This guide provides an engineering-grade analysis of A413’s composition, properties, and applications, demonstrating how its unique characteristics deliver reliable, high-performance components from design to delivery.
- What is A413 Aluminum Alloy?
- A413 Aluminum Alloy Chemical Composition
- Mechanical & Physical Properties of A413 Aluminum
- Key Advantages of A413 in High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
- A413 vs. A380: An Engineering Comparison
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM) with A413 Alloy
- Surface Finishing for A413 Alloy
- Common Applications of A413 Aluminum Castings
- FAQs
- Precision A413 Die Casting from Design to Delivery
- Aluminum Die Casting Services
What is A413 Aluminum Alloy?
A413 (also designated as A14130 by UNS and LM6 in British Standards) is a casting alloy belonging to the 4xx.x series of aluminum alloys, where silicon (Si) is the principal alloying element. The high silicon content, typically between 11.0% and 13.0%, defines its eutectic nature, which means it solidifies at a single, constant temperature rather than over a range. This characteristic is the primary source of its outstanding casting properties.
An Overview of the 4xx.x Series
The Aluminum Association designates the 4xx.x series for alloys where silicon is the main alloying addition. This series is renowned for excellent casting characteristics, including high fluidity and low shrinkage, making these alloys ideal for producing complex shapes via die casting. A413 is arguably one of the most important alloys in this series for high-pressure applications.
A413 Aluminum Alloy Chemical Composition
The performance of A413 is directly tied to its elemental makeup, as specified by standards like ASTM B85. While appearing simple, the balance of its components is precisely controlled to achieve its signature properties.
The Critical Role of High Silicon Content
The defining feature of A413 is its high silicon content (11.0–13.0%). This places it at the eutectic point in the Al-Si system, granting it several key advantages:
- Enhanced Fluidity: The high silicon content significantly lowers the alloy’s melting point and viscosity, allowing it to flow readily into the most complex and thin-walled sections of a die without premature solidification.
- Reduced Solidification Shrinkage: As a eutectic alloy, A413 solidifies with minimal volume change, which drastically reduces the tendency for shrinkage porosity. This is the cornerstone of its excellent pressure tightness.
- Improved Wear Resistance: The hard silicon particles dispersed throughout the aluminum matrix contribute to good wear resistance in finished parts.
Composition Table (ASTM B85 Standard)
| Element | Content (wt%) |
|---|---|
| Silicon (Si) | 11.0 – 13.0 |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤1.3 |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤1.0 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤0.35 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | ≤0.10 |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤0.50 |
| Zinc (Zn) | ≤0.50 |
| Tin (Sn) | ≤0.15 |
| Other, Total | ≤0.25 |
| Aluminum (Al) | Balance |
Mechanical & Physical Properties of A413 Aluminum
A413 offers a robust set of mechanical and physical properties in the as-cast (F) condition, making it suitable for a wide array of demanding applications without the need for heat treatment.
Mechanical Properties Table (As-Cast)
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 240 – 290 MPa |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 130 – 150 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 1.5 – 3.5% |
| Brinell Hardness | 80 HB |
| Fatigue Strength | 130 MPa |
| Shear Strength | 170 MPa |
Values can vary with casting parameters.
Physical and Thermal Properties Table of A413 Aluminum
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.60 – 2.68 g/cm³ |
| Melting Range (Solidus-Liquidus) | 560 – 580 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 120 – 121 W/m-K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 21 µm/m-K |
Key Advantages of A413 in High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
A413 is not just another casting alloy; its properties make it uniquely suited for the rigors of HPDC and the demands of high-performance components.
- Unmatched Pressure Tightness: This is the hallmark of A413. The eutectic composition ensures uniform solidification with minimal shrinkage, leading to a dense, low-porosity microstructure. This makes A413 the material of choice for components that must contain gases or fluids under pressure, such as pneumatic valve bodies, hydraulic cylinders, and fluid reservoirs.
- Superior Castability & Fluidity for Complex Geometries: The alloy’s excellent fluidity allows for the production of parts with exceptionally thin walls (down to 1.5 mm) and intricate details that would be impossible with many other alloys. This attribute provides designers with greater freedom and can reduce the need for subsequent machining operations, lowering overall production costs.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: A413 forms a stable, passive alumina (Al₂O₃) surface layer that provides excellent protection against atmospheric and chemical corrosion. Its low copper content further enhances its resistance compared to other high-strength casting alloys like A380, making it suitable for components exposed to the elements.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: While not as strong as some heat-treated alloys, A413 provides a very favorable balance of strength and low density. This makes it a valuable material for lightweighting initiatives in the automotive and aerospace industries, where reducing component mass without compromising structural integrity is critical.
A413 vs. A380: An Engineering Comparison
A380 is often considered the workhorse of the aluminum die casting industry. However, for specific applications, A413 presents a superior alternative. The primary difference lies in the main alloying elements. A413 is an Al-Si eutectic alloy (11-13% Si), whereas A380 is an Al-Si-Cu alloy with lower silicon (7.5-9.5%) but significantly more copper (3.0-4.0%).
This fundamental difference dictates their performance:
- Choose A413 for Pressure Tightness: If your component must be leak-proof, A413 is the clear winner.
- Choose A413 for Intricate, Thin-Walled Parts: Its superior fluidity ensures complete die filling.
- Choose A413 for Better Corrosion Resistance: Its lower copper content gives it an edge in corrosive environments.
- Consider A380 for Higher Strength: A380’s higher copper content gives it a greater ultimate tensile strength.

Property Comparison Table: A413 vs. A380
| Property | A413 (AlSi12) | A380 (AlSi8Cu3) | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Tightness | Excellent | Good | A413 |
| Castability (Fluidity) | Excellent | Very Good | A413 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Very Good | Good | A413 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | ~290 MPa | ~324 MPa | A380 |
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) with A413 Alloy
To fully leverage the benefits of A413, consider these DFM principles during the design phase:
- Wall Thickness: Maintain uniform wall thickness where possible. A413 allows for thinner walls than most alloys.
- Draft Angles: Incorporate adequate draft angles (typically 1-2 degrees) on all surfaces parallel to the die opening direction.
- Fillets and Radii: Use generous fillets and radii on all inside and outside corners to improve metal flow and reduce stress concentrations.
- Parting Line: Strategically place the parting line to simplify die construction and minimize its impact on the part’s appearance and function.
Surface Finishing for A413 Alloy
While A413 aluminum offers excellent as-cast corrosion resistance, many applications require additional surface treatments for enhanced protection, wear resistance, or specific aesthetic properties. The high silicon content of A413 influences the suitability of certain finishing processes.
Here are the most common surface treatments for A413 die castings:
- Powder Coating & Liquid Painting: These are the most common and effective methods for applying a durable decorative or protective layer. A proper pretreatment, such as a chromate or non-chromate conversion coating, is crucial to ensure excellent adhesion and prevent blistering or peeling.
- Conversion Coating (e.g., Alodine/Chromate): This chemical treatment creates a thin, inert surface layer that significantly enhances corrosion resistance and serves as an excellent primer for paint and powder coating. It is often specified for parts that will be painted or used in harsh environments.
- Anodizing: Decorative anodizing on A413 is challenging. The high silicon content results in a non-uniform, often dark gray finish, as silicon particles do not anodize. However, hard anodizing (Type III) is feasible and can be applied to improve surface hardness and wear resistance, although the appearance will be dark and functional rather than decorative.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: For applications requiring superior wear resistance, lubricity, or corrosion protection, electroless nickel plating is a viable option. It requires a specialized pretreatment process (typically a zincate bath) to achieve strong adhesion on the aluminum substrate.
- Shot Blasting & Bead Blasting: These mechanical processes are used to clean the casting surface, remove minor imperfections, and create a uniform matte texture. They are typically used as a preparatory step before painting, powder coating, or plating.
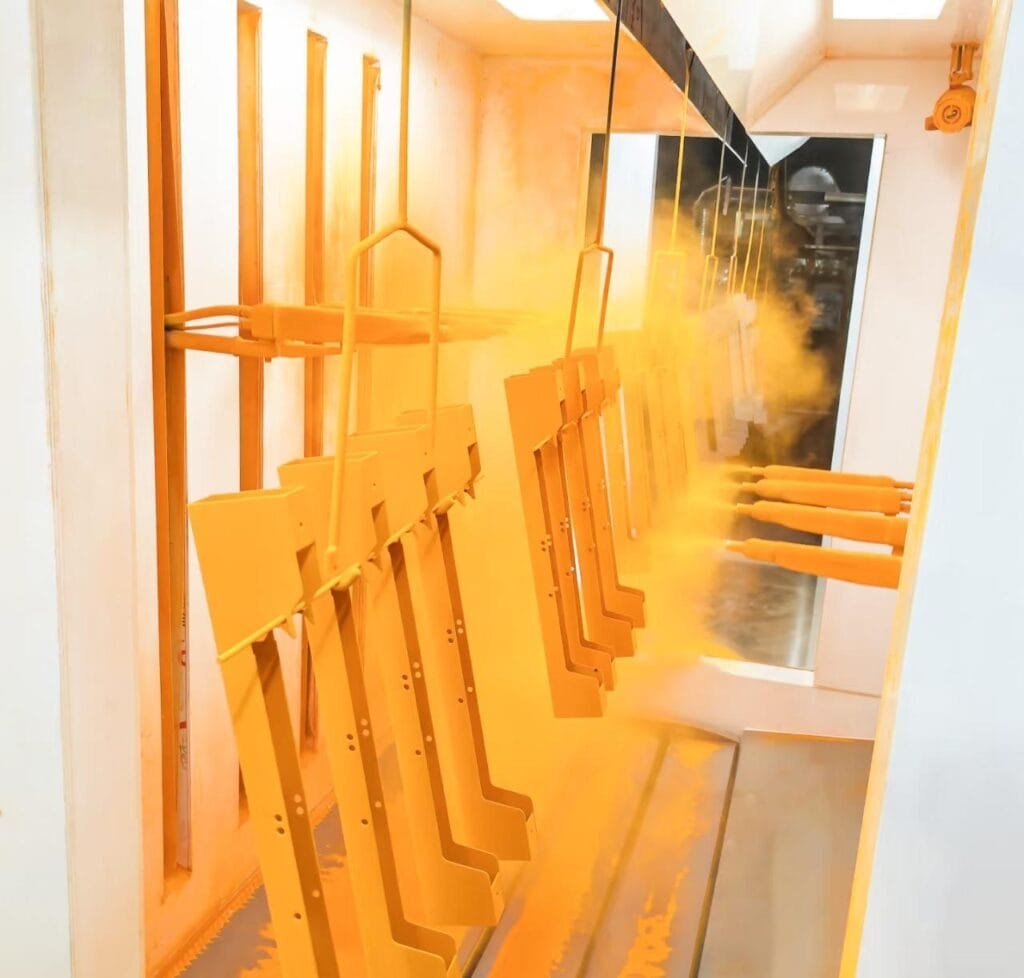

Common Applications of A413 Aluminum Castings
- Automotive: Transmission cases, engine components, hydraulic systems.
- Aerospace: Housings and structural components.
- Electronics: Heatsinks and housings, leveraging its good thermal conductivity.
- Marine: Components exposed to saltwater, due to its enhanced corrosion resistance.
- General Engineering: Pneumatic and hydraulic valve bodies, pump housings, and pressure vessels.

FAQs
Precision A413 Die Casting from Design to Delivery
Choosing A413 aluminum alloy is a critical first step for demanding applications. However, realizing its full potential requires a manufacturing partner dedicated to precision. By integrating advanced DFM principles, process simulation, and rigorous quality control, we ensure your A413 components meet the highest standards for pressure tightness, structural integrity, and dimensional accuracy.
For components that demand superior pressure tightness and intricate designs, A413 aluminum alloy delivers unparalleled performance. Ready to discuss your next high-pressure die casting project? Contact us for an engineering review and a competitive quote.
Aluminum Die Casting Services
Learn more about our aluminum high pressure die casting services in China.